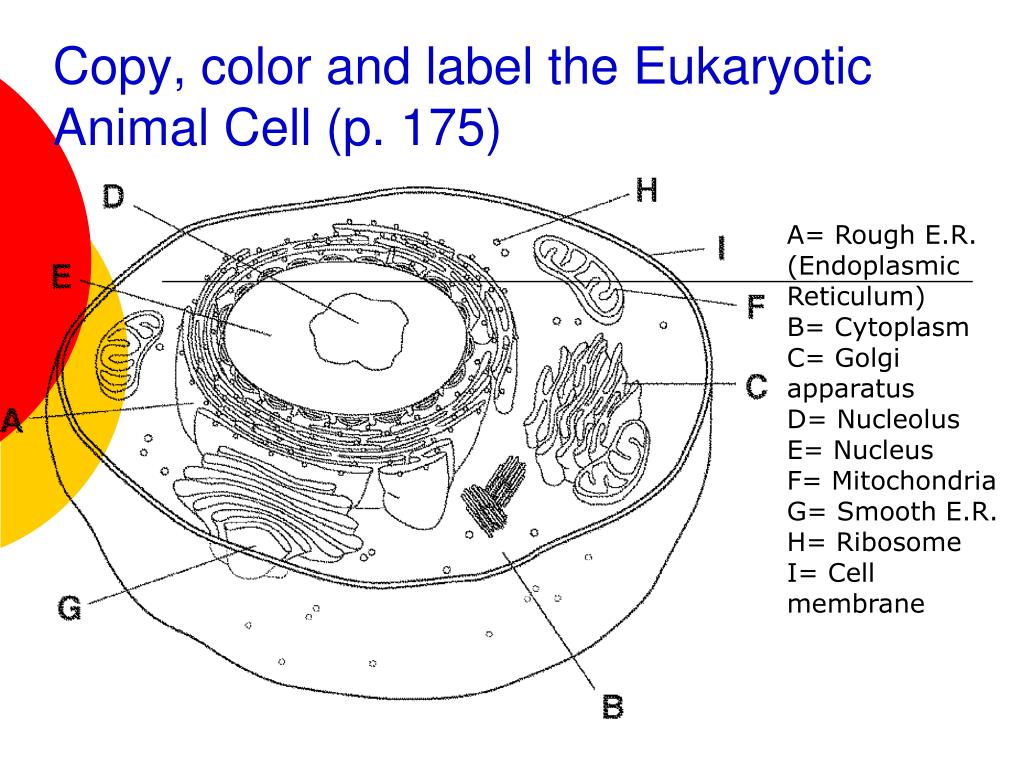
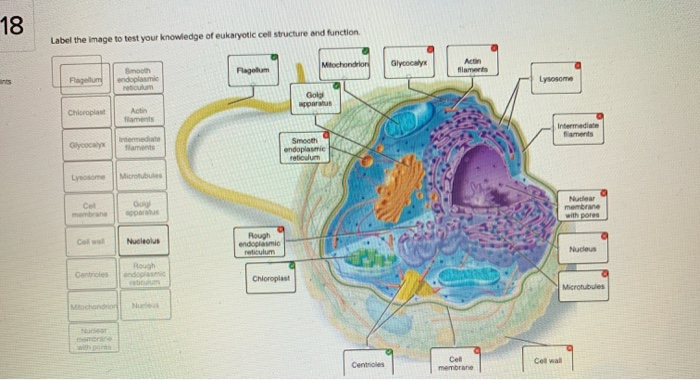
38 label eukaryotic cell
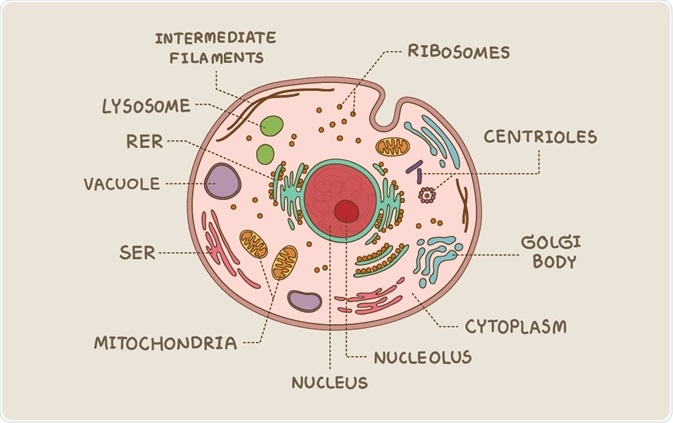
Free Anatomy Quiz - The anatomy of the cell - Quiz 1 The quiz above includes the following features of a typical eukaryotic cell : centrioles, the cytoplasm, the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, the golgi complex, lysosomes, microfilaments, mitochondria, the nucleolus, the nucleus, the nuclear membrane, pinocytotic vesicles, the plasma membrane, ribosomes and vacuoles. Label the Eukaryotic Cell - Printable - PurposeGames.com This is a printable worksheet made from a PurposeGames Quiz. To play the game online, visit Label the Eukaryotic Cell Download Printable Worksheet Please note! You can modify the printable worksheet to your liking before downloading. Download Worksheet Include correct answers on separate page About this Worksheet
Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Quiz - PurposeGames.com This is an online quiz called Eukaryotic Cell Labeling There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Total Points 0 Get started! Today's Rank -- 0 's Points Points 10 to score the 10 points available Add to Playlist

Label eukaryotic cell
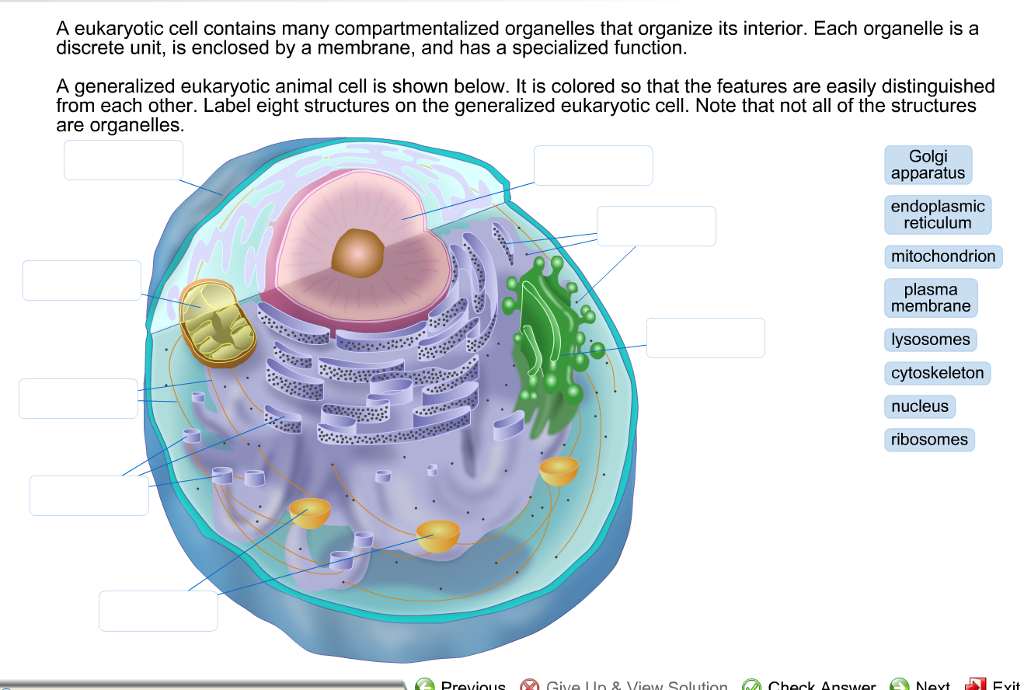
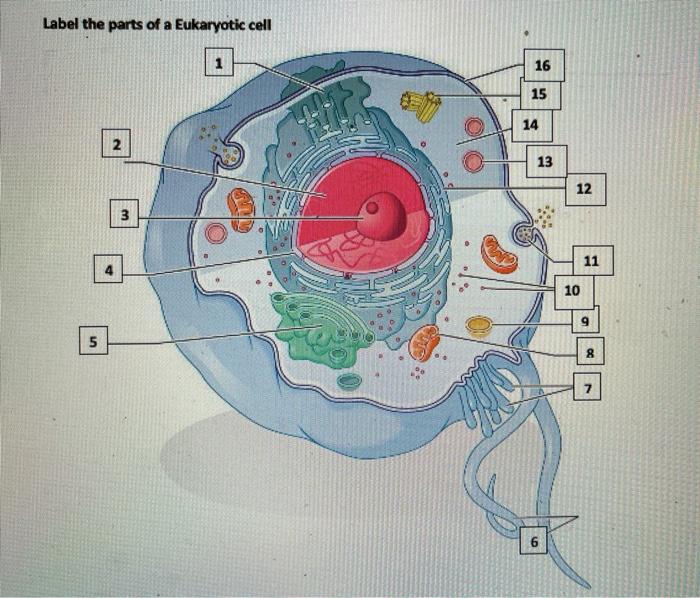
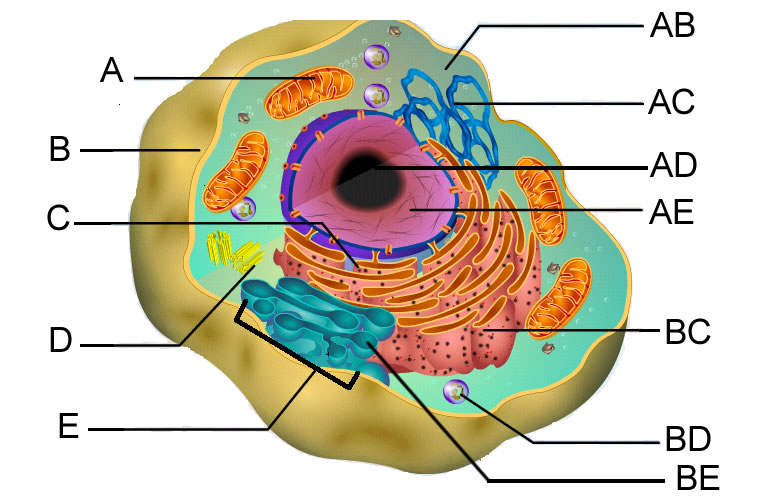
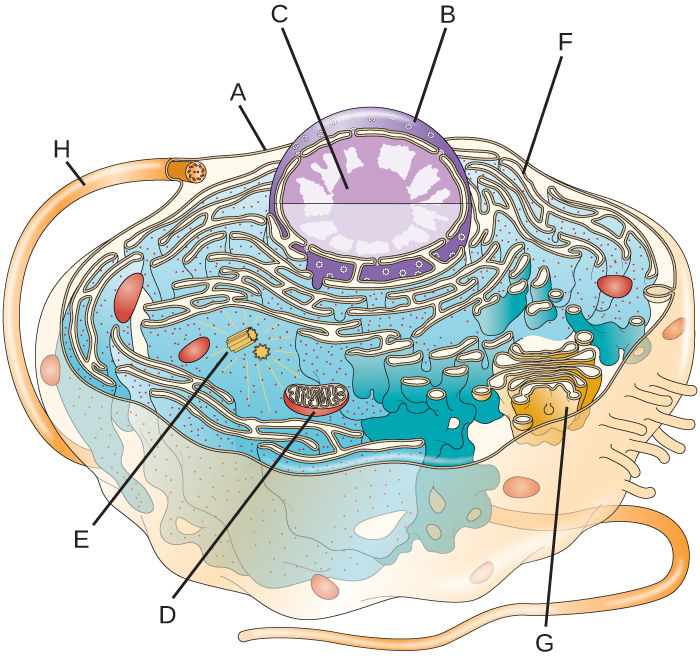
Solved: Label the following parts of this eukaryotic cell ... - Chegg Membrane is a structural component that separates intracellular and extracellular environment by means of plasma membrane. Inside the eukaryotic cell (nucleus having), numerous cell organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus, etc. are present, which serve various functions. Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Diagram, and Examples - Research Tweet Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are Algae, Fungi, Plants, Protists and Animals. What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotes contain a nucleus, which is a huge organelle containing the genetic information. 4,458 Eukaryotic cell Images, Stock Photos & Vectors - Shutterstock 4,420 eukaryotic cell stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See eukaryotic cell stock video clips Image type Orientation People Artists Sort by Popular Biology Animals and Wildlife Healthcare and Medical eukaryote cell nucleus anatomy organelle plasma membrane prokaryotes Next of 45
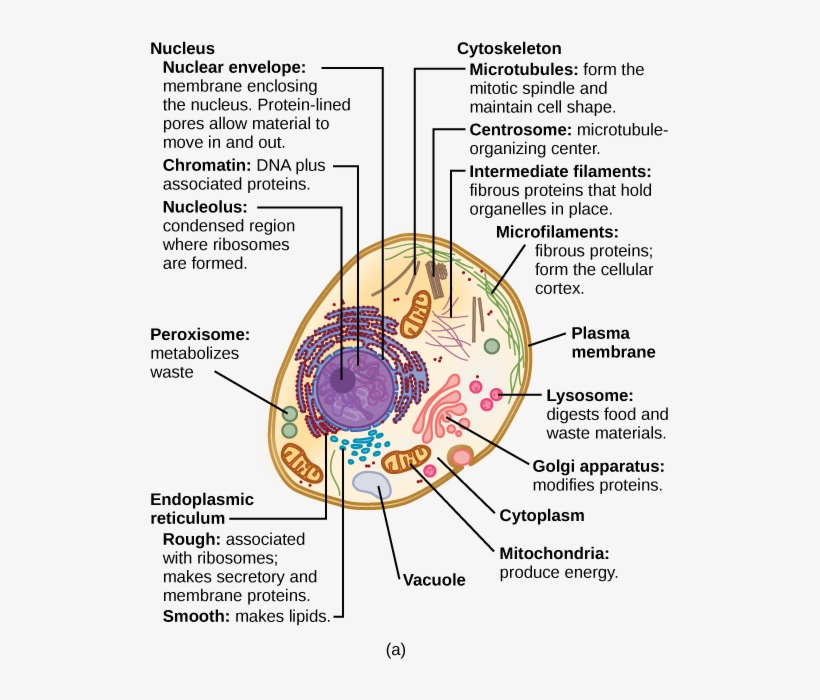
Label eukaryotic cell. Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes Two major regions can be found in a cell. The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram - Science Prof Online Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles | Kenhub The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. The major differences between animal and plant cells will be explored as well. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, Structure & Function (with Analogy ... Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus.
2.3: Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function - Biology LibreTexts By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others. Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles. 1. True 2. False. Answer: Organelles are the specialised and organised structures in a living cell. These may be bound by a single or double membrane (Exception is ribosomes which are non-membranous cell organelles present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes). Membrane-bound cell organelles ... Eukaryotic Cell: Colour & label worksheet | Teaching Resources A-Level 2016 Biology Eukaryote Cell Worksheet Worksheet (pdf) aimed at A-Level Biology students studying AQA Cell Structure topic. The pack contains a detailed, labelled diagram an animal cell. Students can colour the diagram and add detail to the label boxes - with an answer sheet for the teacher to make use of. Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells - ThoughtCo May 04, 2019 · Most plant cell types are capable of differentiation. Growth . Animal cells increase in size by increasing in cell numbers. Plant cells mainly increase cell size by becoming larger. They grow by absorbing more water into the central vacuole. Cell Wall . Animal cells do not have a cell wall but have a cell membrane. Plant cells have a cell wall ...
Eukaryotic Cell Labeled Diagram | Quizlet Eukaryotic Cell Labeled STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity + − Created by tiffany_foret Terms in this set (11) Cytoskeleton maintains shape of cell and provides movement Mitochondria Carries out cellular respiration to release energy from foods. (powerhouse of the cell/ATP) Peroxisome Cell Labeling - The Biology Corner Two line drawings of eukaryotic cells for students to label organelles and structures. Cell Labeling . This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. ... Eukaryotic cell questions (practice) | Khan Academy Practice: Eukaryotic cell questions. This is the currently selected item. Cellular organelles and structure. Characteristics of eukaryotic cells. The nucleus. Mitochondria. Endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus. Lysosomes and peroxisomes. Epithelial and connective tissue. Next lesson. Eukaryotic Plant Cell (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the ultrastructure and functions of a typical eukaryotic plant cell. A typical eukaryotic plant cell is usually spherical, polyhedral, box-like or elongated in shape with a diameter of about 0.01 mm to 0.1 mm. It consists of three parts: ADVERTISEMENTS: (A) Cell Wall (B) Cytoplasm, and (C) […]
Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - GCSE Combined Science ... Plant cells. This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below – the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope.
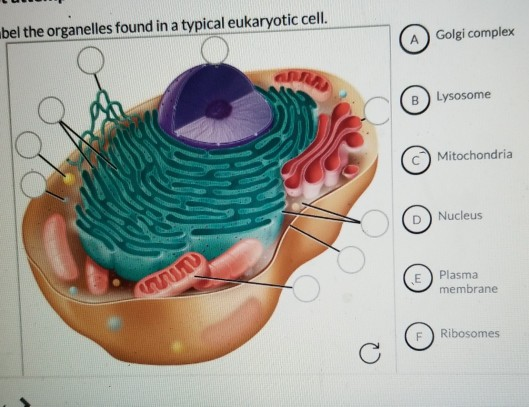
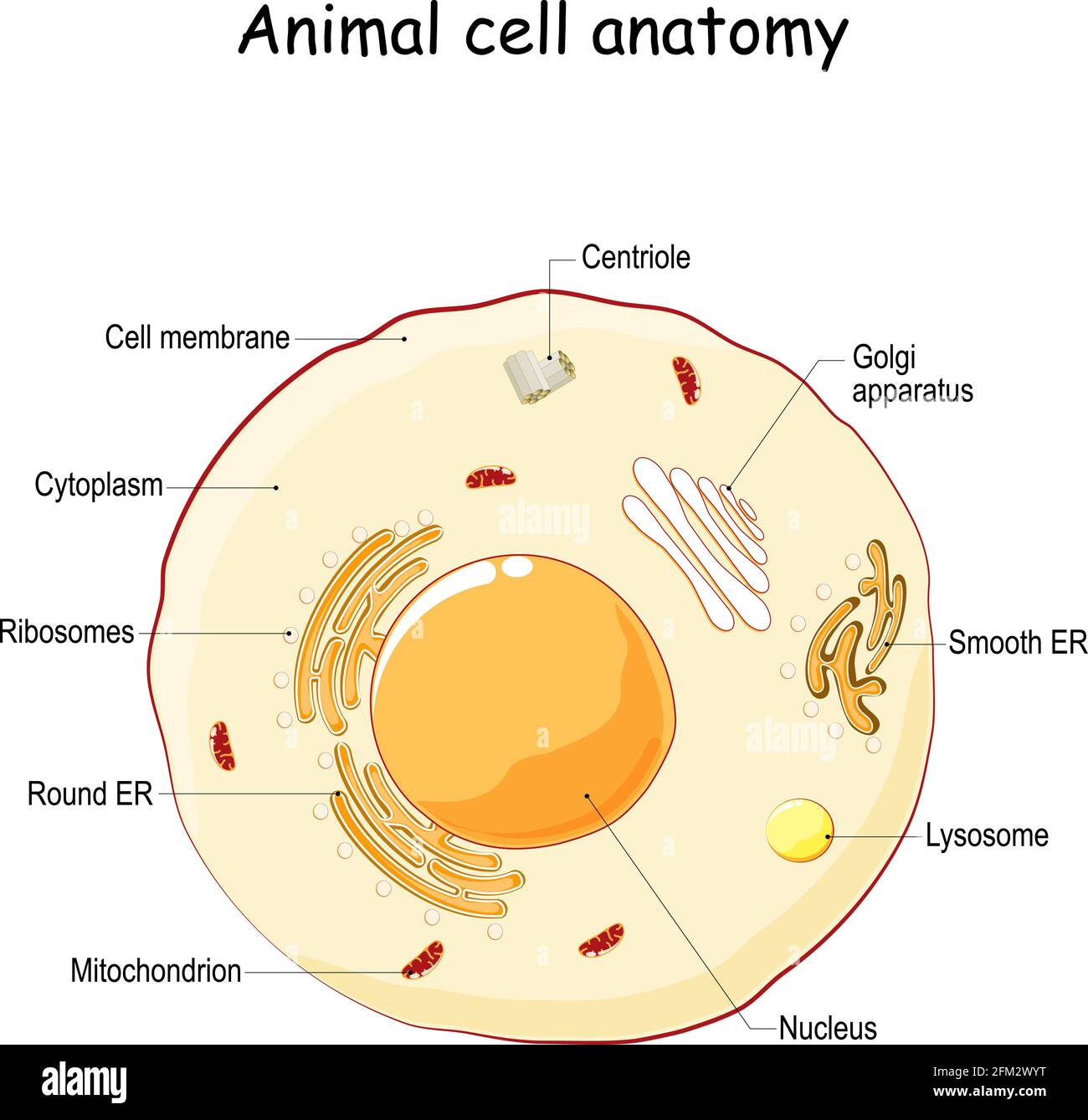
A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Where, prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else.
Eukaryotic cell diagram labelling game - ESL Games Plus A eukaryotic cell produces many substances. For instance, the ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) create proteins. The ER is also capable of synthesizing lipid molecules. To ensure that there's enough energy to power all of these activities, eukaryotic cells also have tiny power-generating plants called mitochondria.
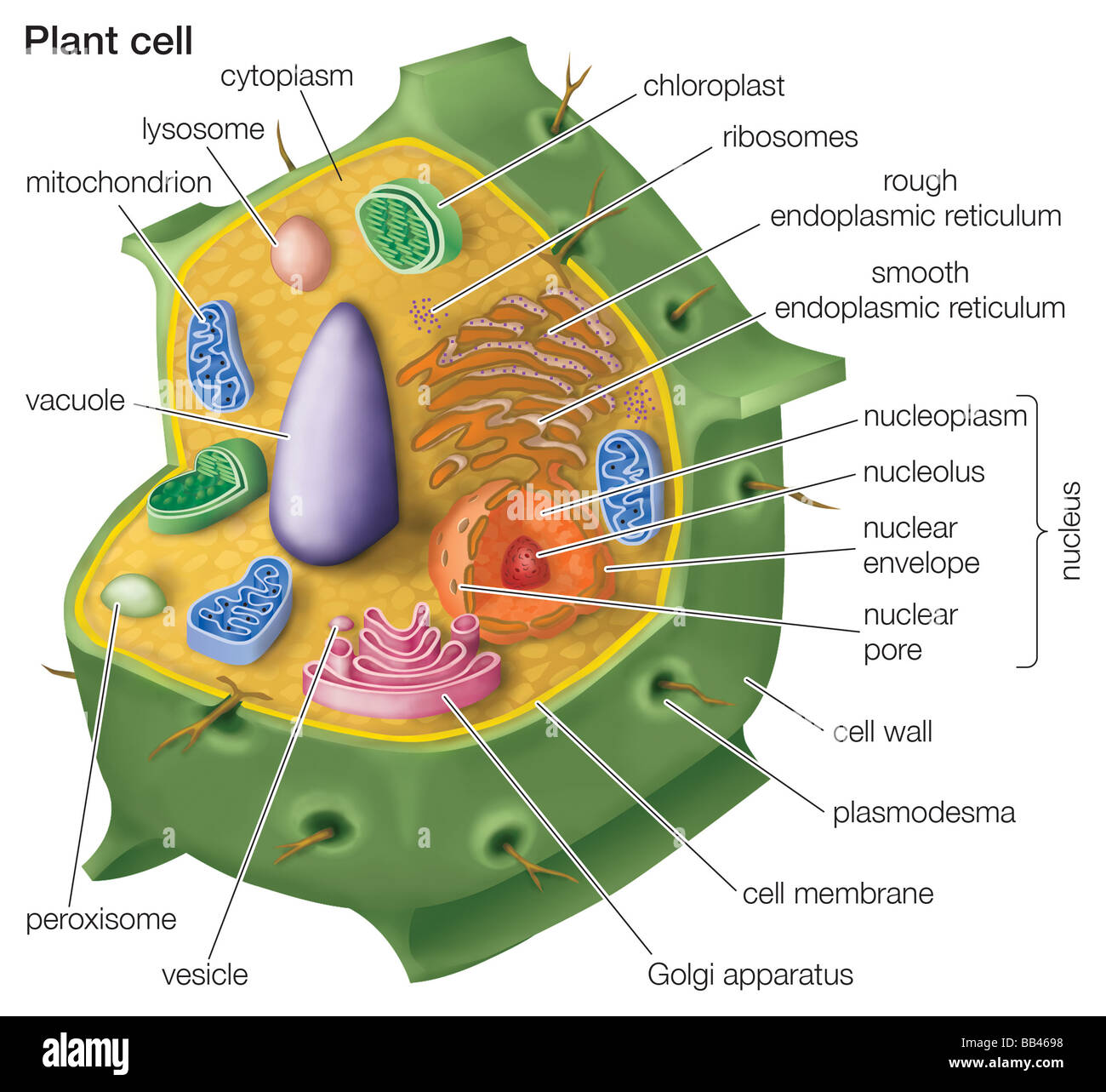
Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends Plant cells contain many organelles such as ribosomes, the nucleus, the plasma membrane, the cell wall, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. In addition, plant cells differ from animal cells in a number of key ways. Examining a diagram of the plant cell will help make the differences clearer. Let's go over the individual components of plant cells ...
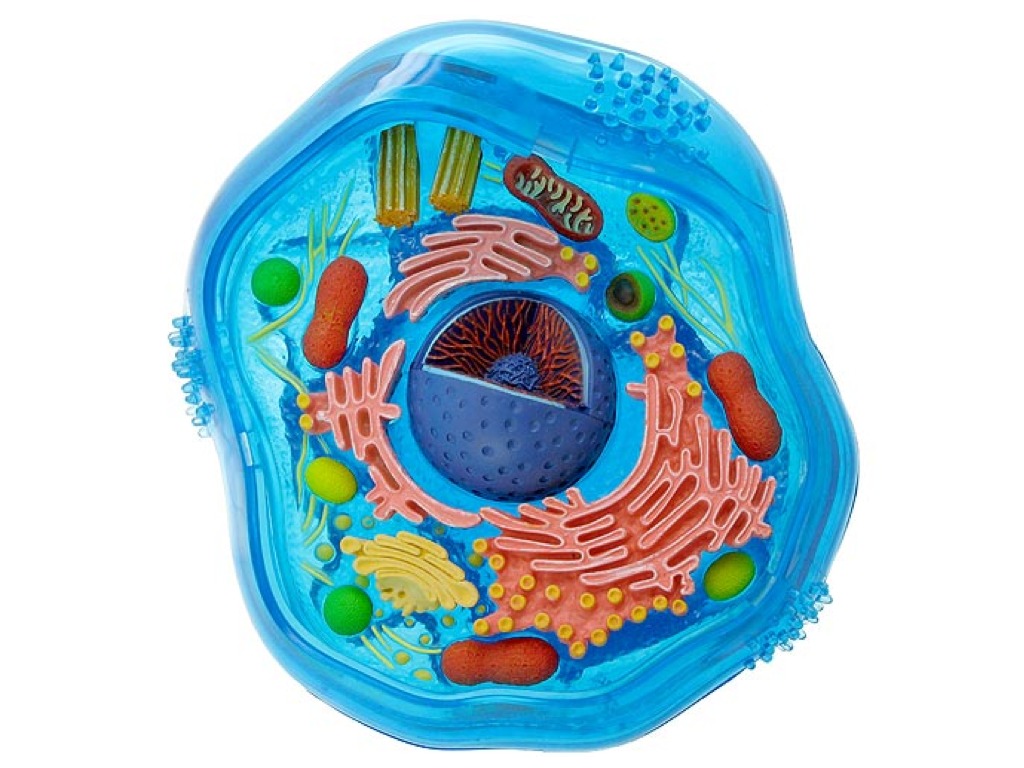
Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Throughout the eukaryotic cell, especially those responsible for the production of hormones and other secretory products, is a vast network of membrane-bound vesicles and tubules called the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER for short. The ER is a continuation of the outer nuclear membrane and its varied functions ...
Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota. They can maintain different environments in a single cell that allows them to carry out various metabolic reactions.
DNA Structure - YouTube Learn about the structure of DNA and how to recognize all the parts in this video!
PHSchool.com Retirement–Prentice Hall–Savvas Learning Company PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobe’s decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support.
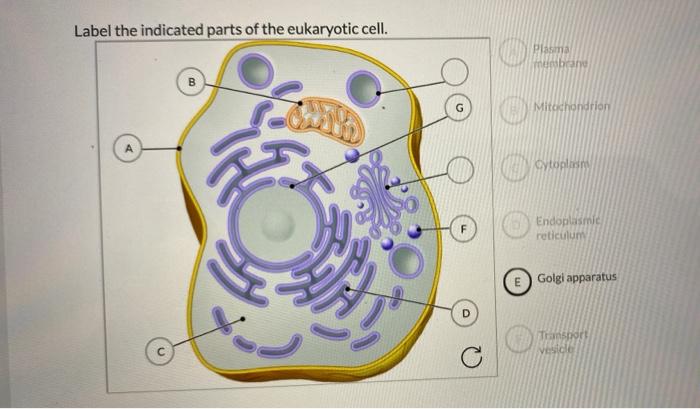
Solved - label a eukaryotic cell - plant and animal | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! - label a eukaryotic cell - plant and animal (all cellular structures and organelles) - draw and label the structural details of mitochondria and chloroplasts. 1)the pathway for secretory, membrane, or lysosomal proteins through the endo-membrane system2) 2)the motor protein "walking" models for transport and ...
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe A eukaryotic cell is an advanced type of cell that has a well-defined nucleus and multiple membrane-bound organelles. DNA is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration.
Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell nucleus: A cell's information center, the cell nucleus is the most conspicuous organelle found in a eukaryotic cell. It houses the cell's chromosomes , and is the place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis ( transcription ) occur.
Eukaryotic Cells Quiz - ProProfs Quiz Eukaryotic cells are known to have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane, and they form huge and complex organisms. Protozoa, plants, fungi, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom of Eukaryota. These questions will give you an even better understanding of eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
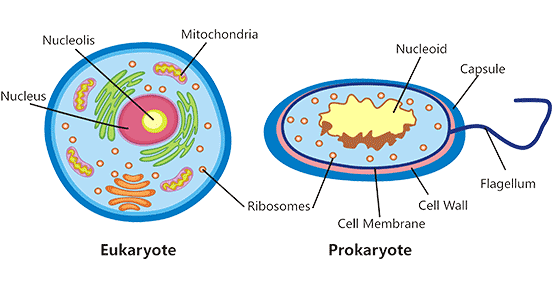
Prokaryotic cell to label - Labelled diagram - Wordwall Verbind ieder label met de juiste plek in de afbeelding.. nucleoid region, pili, ribosomes, flagellum, plasmid, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cell wall, capsule.
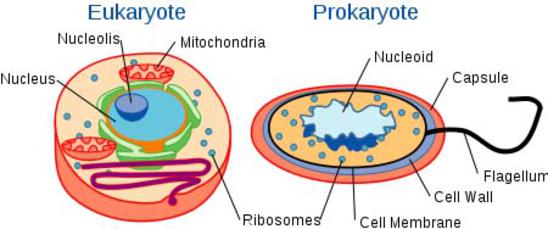
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - BYJUS The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells. Another major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells are exclusively ...
Label Eukaryotic Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Label Eukaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Eukaryotic Cells | Structure, Differences, Facts & Summary Eukaryotic cells are those cells that contain a nucleus and organelles enclosed by a plasma membrane. They are found in all the eukaryotic organisms. The eukaryotic organisms include four kingdoms; kingdom Protista, kingdom Fungi, kingdom Plantae and kingdom Animalia. Most of the eukaryotes are multicellular organisms having complex forms.
DNA Replication - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf DNA Polymerases. DNA polymerase was first identified in lysates of E.coli by Arthur Kornberg in 1956. The ability of this enzyme to accurately copy a DNA template provided a biochemical basis for the mode of DNA replication that was initially proposed by Watson and Crick, so its isolation represented a landmark discovery in molecular biology.
4,458 Eukaryotic cell Images, Stock Photos & Vectors - Shutterstock 4,420 eukaryotic cell stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See eukaryotic cell stock video clips Image type Orientation People Artists Sort by Popular Biology Animals and Wildlife Healthcare and Medical eukaryote cell nucleus anatomy organelle plasma membrane prokaryotes Next of 45
Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Diagram, and Examples - Research Tweet Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are Algae, Fungi, Plants, Protists and Animals. What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotes contain a nucleus, which is a huge organelle containing the genetic information.
Solved: Label the following parts of this eukaryotic cell ... - Chegg Membrane is a structural component that separates intracellular and extracellular environment by means of plasma membrane. Inside the eukaryotic cell (nucleus having), numerous cell organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus, etc. are present, which serve various functions.













:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12788/histology-eukaryotic-cell_english.jpg)
Post a Comment for "38 label eukaryotic cell"